Ever wondered how a single strand of optical fiber can carry the world’s internet traffic, countless Zoom calls, and your favorite Netflix shows—all at once? The answer lies in the magic of Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM). If you’re struggling to keep up with the jargon of FWDM, CWDM, or DWDM, or just want to know how modern networks handle ever-growing data demands, you’re in the right place. Let’s break down WDM in simple terms, so you can see how it powers everything from your home Wi-Fi to global communications.
What is Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)?
Imagine trying to fit more cars on a highway without building new lanes. That’s the challenge network engineers face with optical fibers. WDM is the clever solution: instead of one “lane” (wavelength) per fiber, WDM lets you send multiple “cars” (data streams), each on its own color of light, down the same fiber. By adding a multiplexer and demultiplexer at each end, different data channels travel simultaneously, each on its own wavelength, multiplying the fiber’s capacity without laying new cables.
Why Should You Care?
Upgrades bandwidth without digging up roads or laying new fiber.
Supports high-speed internet, cloud services, and streaming.
Essential for businesses, data centers, and telecom providers facing explosive data growth.
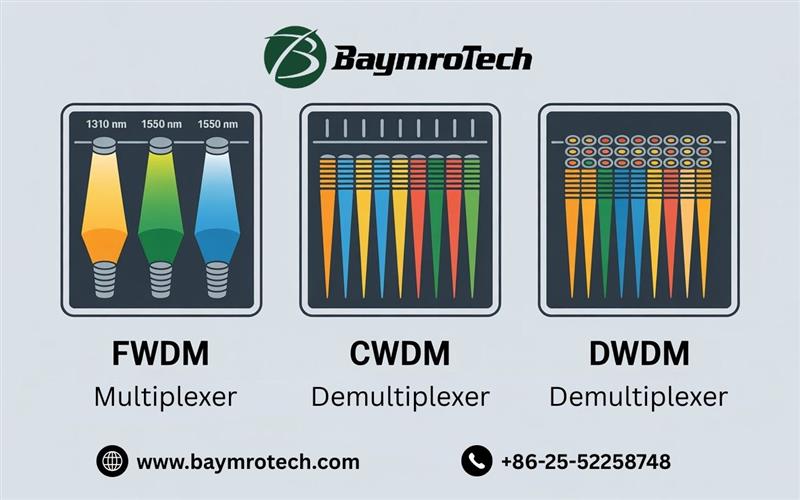
Types of WDM: FWDM, CWDM, DWDM Explained
You’ve probably seen acronyms like FWDM, CWDM, and DWDM thrown around. Here’s what they mean, without the alphabet soup headache.
FWDM (Filter Wavelength Division Multiplexing)
FWDM uses thin-film filter (TFF) technology to combine or separate different wavelengths of light. It’s like a traffic cop for light, directing each color (wavelength) to its proper lane. FWDMs are compact, reliable, and widely used in applications like fiber amplifiers, FTTX systems, and telecom networks. They offer:
Wide channel bandwidth
Low insertion loss (less signal loss)
High channel isolation (minimal interference)
Excellent stability in tough environments
FWDM devices typically have three ports: one for incoming signals, one for passing specific wavelengths, and one for reflecting unwanted wavelengths. This makes them ideal for precise, cost-effective network setups.
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing)
CWDM is the “budget-friendly” cousin in the WDM family. It typically supports up to 18 channels, each spaced widely apart, making it perfect for shorter distances and less demanding environments. Think of it as a city bus—efficient, but not built for cross-country trips. CWDM is popular for metro networks and enterprise connections where cost matters.
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing)
DWDM is the powerhouse. It packs up to 88 or more channels closely together, using precision lasers for long-haul, high-capacity data transmission. Imagine a bullet train with tightly scheduled departures—DWDM is built for speed and distance, handling massive volumes of data for core networks, data centers, and telecom giants.
How Does Fused WDM Work?
Fused WDM (FWDM) uses a “fused biconic taper” (FBT) technique. Two optical fibers are heated and stretched until they fuse together, creating a region where different wavelengths can be combined or split with minimal loss. This process allows engineers to direct specific wavelengths to different fibers, enabling efficient signal routing for dual-wavelength systems (like 1310 nm and 1550 nm for telecom).
Key specs for fused WDMs:
Operating wavelength: typically 1310/1550 nm
Insertion loss: ≤0.8 dB (lower is better)
Isolation: ≥40 dB (higher is better)
Operating temperature: -40°C to +85°C (built tough!)
Why Is WDM So Important Today?
The world’s hunger for data is insatiable. With 5G, AI, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) all demanding more bandwidth, WDM is more crucial than ever. The global WDM market is booming—valued at over $5.3 billion in 2024 and projected to nearly double by 2034, thanks to investments in optical infrastructure and the expansion of 5G networks.
WDM isn’t just for telecom giants. Businesses, hospitals, and government agencies rely on WDM to:
Maximize existing fiber investments
Ensure secure, high-capacity connections
Future-proof their networks as data needs grow
Real-World Example: How WDM Powers Your Everyday Life
Picture this: You’re streaming a live sports game, your partner is on a video call, and your kids are gaming online—all without a hiccup. Behind the scenes, WDM technology is juggling these streams, keeping your home connected and lag-free. For businesses, WDM ensures mission-critical data moves securely and efficiently, whether it’s financial transactions or medical records.
Practical Tips: Choosing the Right WDM Solution
Assess your distance and bandwidth needs: CWDM for short, cost-sensitive links; DWDM for long-haul, high-capacity demands.
Consider environmental factors: FWDM and fused WDMs are robust for harsh conditions.
Plan for growth: Choose scalable solutions that can expand as your data needs increase.
For more details on choosing the right WDM components, check out our WDM product selection guide and see how Baymrotech’s industry solutions can help your business stay ahead.
Want to Dive Deeper?
Learn how thin-film filter technology is revolutionizing optical networks in this industry overview.
Explore the differences between Dark Fiber and Lit Fiber and why WDM is key to both in this expert guide.
See real-world performance specs for fused WDMs in this comprehensive guide.
Conclusion:
WDM—The Unsung Hero of Modern Connectivity
Wavelength Division Multiplexing quietly powers the digital world, making high-speed, reliable connections possible without endless new construction. Whether you’re a network engineer, IT manager, or just a curious tech enthusiast, understanding WDM gives you a front-row seat to the future of connectivity.
Ready to supercharge your network? Explore our WDM solutions or contact our team for expert advice tailored to your needs. Have questions or want to share your experience with WDM? Drop a comment below—we’d love to hear from you!




